Retinal Detachment
>
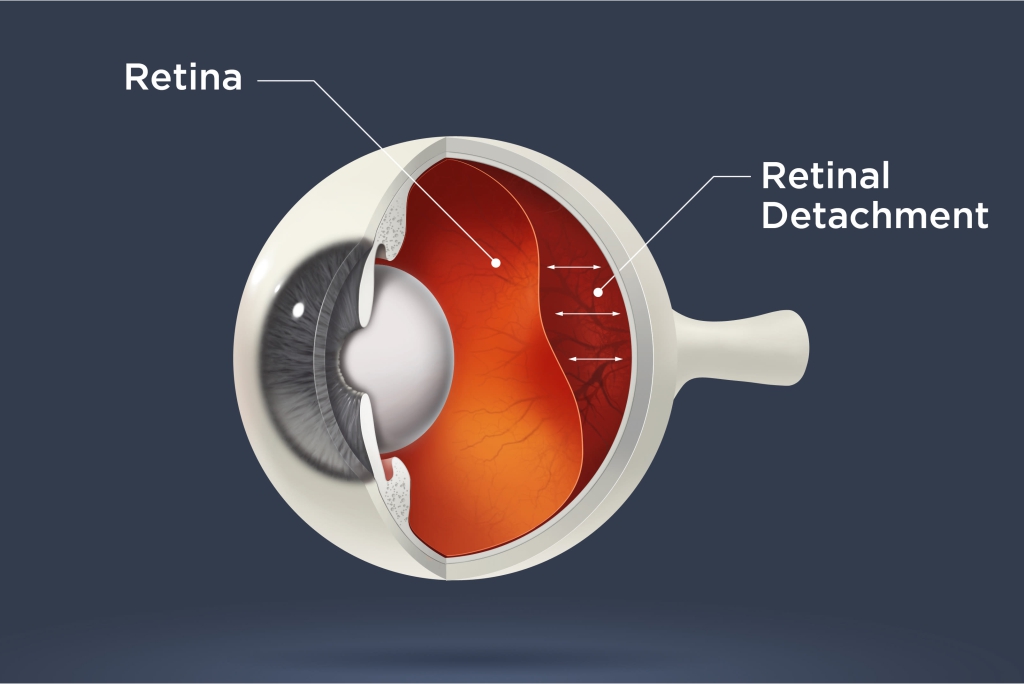
It is a condition in which Retina gets separated or pulled away from its normal position.
Retinal detachment is an emergency condition in which the innermost layer of the eye (which is called as retina) gets detached from the choroid (middle layer of the eye).
What Occurs In Retinal Detachment
The detached retina is one of the serious and sight-threatening experience. It occurs when the retina gets separated from its primary supportive tissue. It may lead to permanent vision loss unless soon the retina is reattached.
RISK FACTORS
Ocular Trauma
Trauma may induce tears or breaks in the retina which can result in retinal detachment. The most common cause of monocular blindness seen in young patients is ocular trauma complications.
Myopia
Extreme near-sightedness
Do you find a problem in reading signage or recognizing faces from distance? You could be suffering from myopia, also known as near-sightedness. High levels of near-sightedness can also lead to retinal detachment.

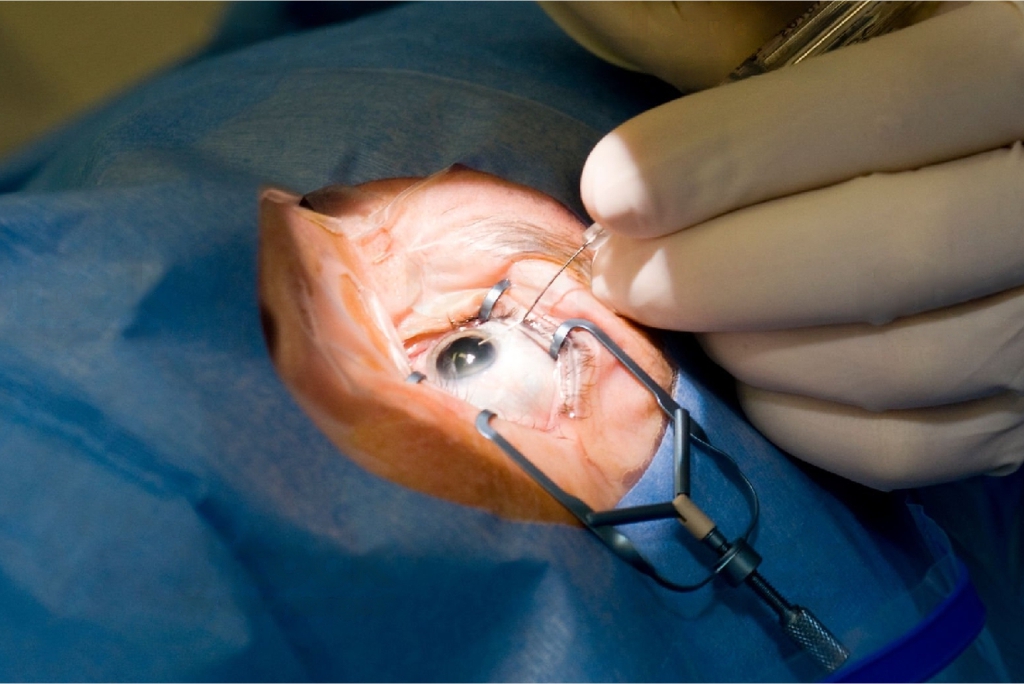
Eye Surgery
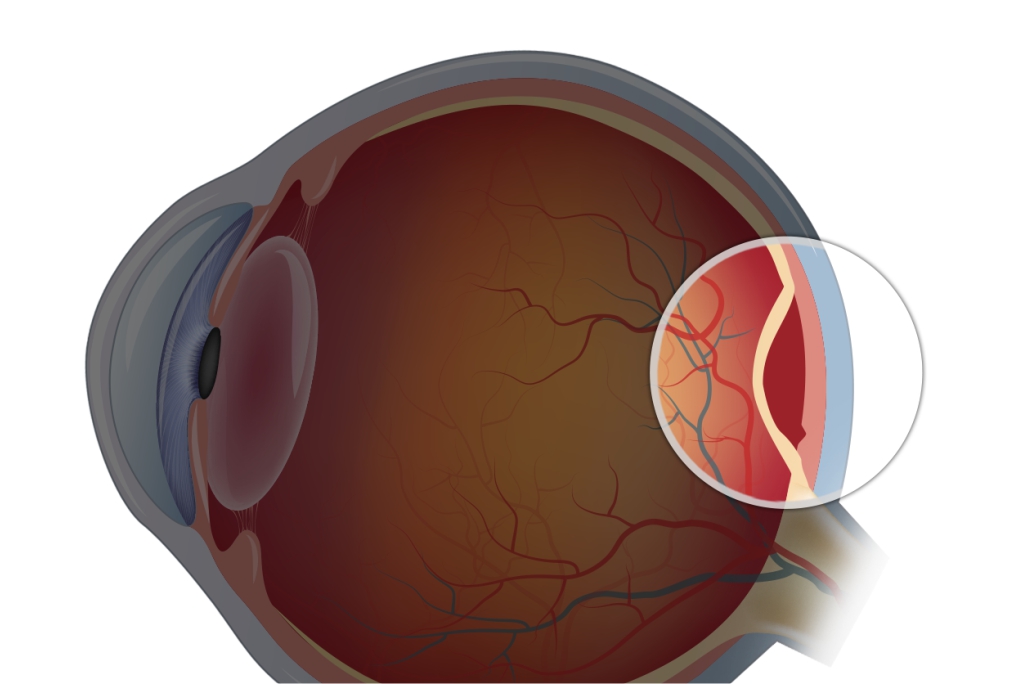
A retinal detachment occurs when fluid gets through a fine tear in the retina, which allows it to detach abnormally from the back wall of the eye.
TREATMENT FOR DETACHED RETINA
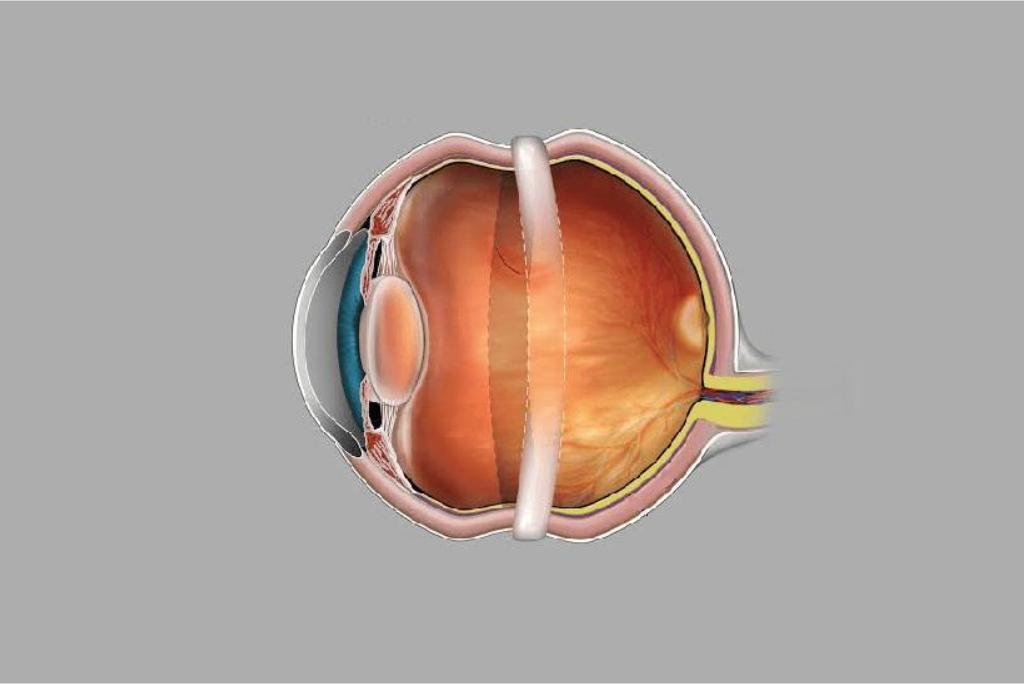
Scleral buckling Surgery
In this surgical procedure, a flexible band is put around the eye to resist the force that detaches out the retina. The fluid under the detached retina is drained, which helps the retina to settle back into its original position.
Pneumatic Retinopexy Procedure
In this procedure, along with retinal laser or cryotherapy, a gas bubble is injected into the vitreous cavity of the eye. The gas bubble drives the detached retina in place against the supporting layer underneath. Our doctor may suggest the patients to maintain a certain head positioning for a few days. Gradually the gas bubble gets replaced by the aqueous of the eye.
Vitrectomy Procedure
This procedure is used to repair a detached retina. The vitreous fluid that holds the retina is extracted from the eye and is replaced by a gas bubble/oil bubble to keep the retina in its place. while the gas bubble slowly gets replaced by aqueous of the eye, the oil bubble is required to drain by another surgical procedure called silicone oil removal (SOR) at a later date.
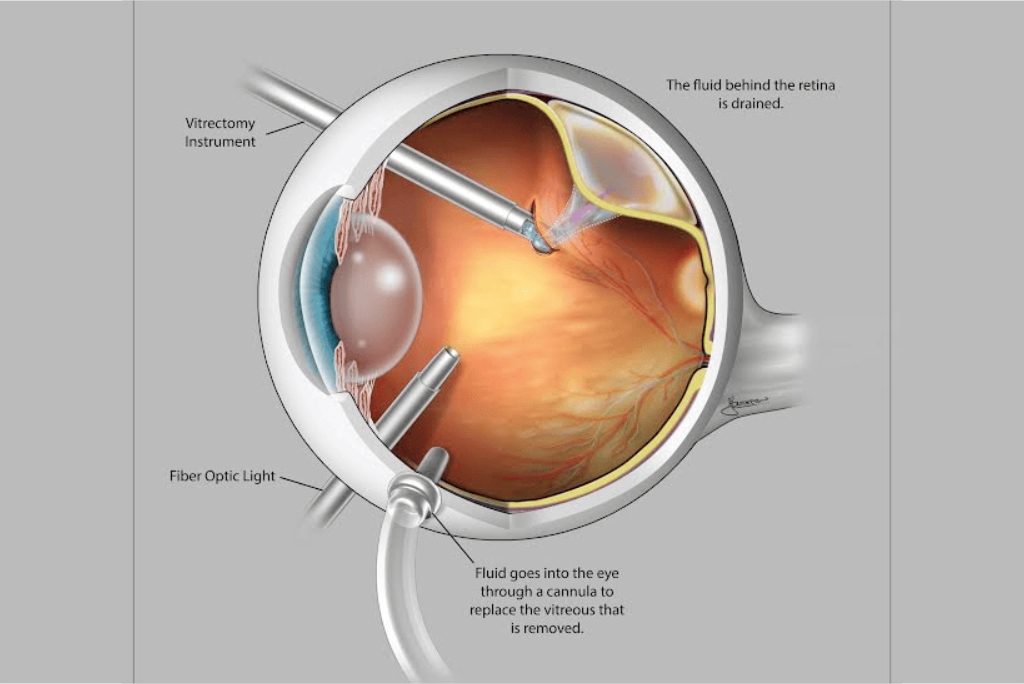
Retinal Detachment Surgery
Patients with retinal detachments must undergo surgery for repositioning the retina in its right place. The method by which retinal detachment is settled depends upon characteristics of the detachment.
Advanced Technology & Diagnostic Tools
Our state of art technology suite provides timely diagnosis & better outcomes for your visual health.
- Retinal Laser (Green)
- Vitrectomy System
- FFA
Frequently Asked Question:
Below are a few frequently asked questions regarding Retinal Detachment.
Can I get my vision back if I have a detached retina?
Sooner the retinal detachment is treated, chances of visual recovery are better. Also, the involvement of the central area of retina (macula) plays an important role in visual recovery. Macular sparing retinal detachments have better visual outcomes.
If I have recently got operated for retinal detachment in the right eye, are there chances of RD in the other eye?
Yes, there is an increased risk of retinal detachment in another eye as well. Dilated retinal evaluation and appropriate management of any predisposing factors in the other eye may help in preventing a detachment in the fellow eye.
Can I check my retina or macula for any signs of damage?
No. Retina is the innermost structure of the eye and requires to be checked with special types of equipment by an ophthalmologist. For right inspection, eye drops are used to dilate the pupil. You can, however, use an Amsler Grid to detect signs of changes in your central vision.
Who is at risk of having a detached retina?
Anyone can have a retinal detachment, but is much more common with high myopic people, those aged above 50 years, family having retinal detachment history and with some retinal disorders.
How risky glaucoma is?
If you have an age over 40 years, have a glaucoma family history or are of African or Asian Hispanic heritage, you have a higher chance of developing glaucoma.
Other risk factors:
• Diabetes or other health concerns
• Hypertension
• High myopia or hyperopia
• Experienced a previous eye injury/surgery
Is glaucoma curable?
Glaucoma causes irreversible visual field losses. The treatment is mainly focused on preserving vision as uncontrolled glaucoma may lead to loss of vision. If it is diagnosed on time and managed carefully, vision loss can be prevented.
